What Is Base Oil Group I, II, and III? full guide by Iran chemical mine
Base oils are the foundation of industrial lubricants, greases, and wax-based products. Understanding their classification helps importers, refiners, and manufacturers select the right grade for their production lines. Iran Chemical Mine — a key exporter of slack wax, foots oil, and related petroleum derivatives — provides this guide to explain the differences among Group I, Group II, and Group III base oils and how they are used in global industries.
What Are Base Oils?
Base oils are the primary ingredient in lubricants, typically making up 70–90% of the total composition. They are derived from crude oil refining or from synthetic processes such as hydrocracking or gas-to-liquid (GTL).
Classification of Base Oils (API System)
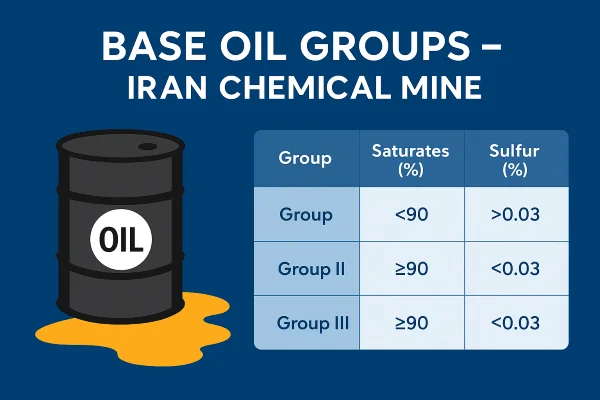
The American Petroleum Institute (API) classifies base oils into five main groups:
| Group | Saturates (%) | Sulfur (%) | Viscosity Index | Refining Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | <90 | >0.03 | 80–120 | Solvent refining |
| II | ≥90 | ≤0.03 | 80–120 | Hydroprocessing |
| III | ≥90 | ≤0.03 | >120 | Severe hydrocracking |
| IV | PAO (synthetic) | – | 125+ | Chemical synthesis |
| V | Other synthetics | – | Variable | Various |
Group I: The Traditional Base Oil
Group I base oils are the oldest and most widely used. Produced via solvent extraction and dewaxing, they have moderate viscosity and higher sulfur content.
- Typical Grades: SN150, SN500, SN600
- Color: Yellow to brown
- Common Uses: Industrial lubricants, hydraulic oils, rubber processing oils, grease manufacturing
- Main Exporters: Iran, Russia, UAE, Southeast Asia
Group II: The Modern Standard
Group II oils are hydrotreated for better purity and oxidation stability.
- Sulfur content: <0.03%
- Color: Clear or water-white
- Applications: Engine oils, transmission fluids, marine lubricants
- Main Producers: Saudi Aramco (Luberef), Chevron, SK Lubricants
Group III: High-Performance & Synthetic-Like
Group III base oils are severely hydrocracked, producing very high viscosity index (120–140) and excellent stability. They are often marketed as synthetic oils, even though they originate from crude oil.
- Applications: Synthetic engine oils, gear oils, aviation lubricants
- Producers: Shell, BP, ADNOC, and other advanced refiners
Global Base Oil Trade and Export Routes
The main export hubs are:
- Middle East (Iran, UAE, Saudi Arabia)
- Asia (Korea, Singapore, India)
- Europe (Belgium, Netherlands)
Iran Chemical Mine supplies base oil, slack wax, and foots oil to Pakistan, Kenya, Tanzania, and Turkey — serving as a reliable bridge between refiners and global end-users.
Related Products and Internal Links
From Group I’s classic lubricants to Group III’s synthetic-grade performance, base oils form the core of industrial lubrication. With expertise in petroleum derivatives and global logistics, Iran Chemical Mine provides consistent, high-quality base oils and related waxes for international buyers.